Mapping Data Types
The Microsoft® SQL Server™ ODBC driver maps SQL Server SQL data types to ODBC SQL data types. The illustration below shows SQL Server SQL data types and the ODBC SQL data types to which they map. It also shows ODBC SQL data types and their corresponding ODBC C data types, and the supported and default conversions.
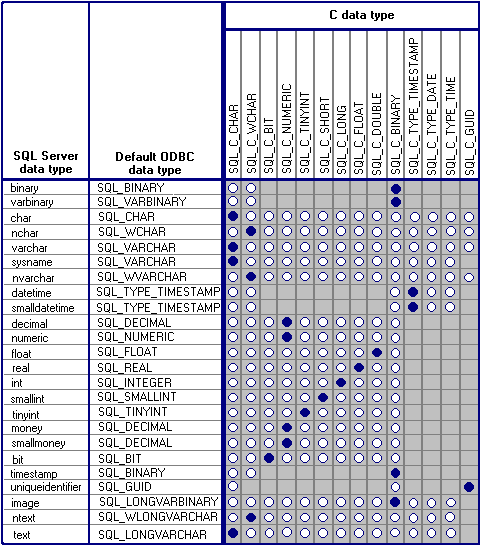
Note The SQL Server timestamp data type maps to the SQL_BINARY or SQL_VARBINARY ODBC data type because the values in timestamp columns are not datetime values, but binary(8) or varbinary(8) values that indicate the sequence of SQL Server activity on the row. If the SQL Server ODBC driver encounters a SQL_C_WCHAR (Unicode) value that is an odd number of bytes, the trailing odd byte is truncated.
Dealing with sql_variant data type in ODBC
The sql_variant data type column can contain any of the data types in SQL Server except large objects (LOBs), such as text, ntext, image. For example, the column could contain smallint values for some rows, float values for other rows, and char/nchar values in the remainder.
The sql_variant data type is similar to the variant data type in Microsoft Visual Basic®.
Retrieving Data from the Server
ODBC does not have a notion of variant types. This limits the use of the sql_variant data type with an ODBC driver in SQL Server 2000. In SQL Server 2000, if binding is specified, the sql_variant data type must be bound to one of the documented ODBC data types. SQL_CA_SS_VARIANT_TYPE, a new attribute specific to the SQL Server ODBC driver, returns the data type of an instance in the sql_variant column to the user.
If no binding is specified, the SQLGetData function can be used to determine the data type of an instance in the sql_variant column.
To retrieve sql_variant data follow these steps.
- Call SQLFetch to position to the row retrieved.
- Call SQLGetData, specifying SQL_C_BINARY for the type and 0 for the data length. This forces the driver to read the sql_variant header. The header provides the data type of that instance in the sql_variant column. SQLGetData returns the size (in bytes) of the value.
- Call SQLColAttribute by specifying SQL_CA_SS_VARIANT_TYPE as its attribute value. This function will return the C data type of the instance in the sql_variant column to the client.
Here is a code segment showing the preceding steps.
while ((retcode = SQLFetch (hstmt))==SQL_SUCCESS)
{
if (retcode != SQL_SUCCESS && retcode != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO)
{
SQLError (NULL, NULL, hstmt, NULL,
&lNativeError,szError,MAX_DATA,&sReturned);
printf ("%s\n",szError);
goto Exit;
}
retcode = SQLGetData (hstmt, 1, SQL_C_BINARY,
pBuff,0,&Indicator);//Figure out the length
if (retcode != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO && retcode != SQL_SUCCESS)
{
SQLError (NULL, NULL, hstmt, NULL, &lNativeError,
szError,MAX_DATA,&sReturned);
printf ("%s\n",szError);
goto Exit;
}
printf ("Byte length : %d ",Indicator); //Print out the byte length
int iValue = 0;
retcode = SQLColAttribute (hstmt, 1, SQL_CA_SS_VARIANT_TYPE, NULL,
NULL,NULL,&iValue); //Figure out the type
printf ("Sub type = %d ",iValue);//Print the type, the return is C_type of the column]
//Set up a new binding or do the SQLGetData on that column with
//the appropriate type
}
If the user creates the binding using SQLBindCol, the driver reads the meta data and the data. The driver then converts the data to the appropriate ODBC type specified in the binding.
Sending Data to the Server
SQL_SS_VARIANT, a new data type specific to the SQL Server ODBC driver, is used for data sent to an sql_variant column. When sending data to the server using parameters (for example, INSERT INTO TableName VALUES (?,?)), SQLBindParameter is used to specify the parameter information including the C type and the corresponding SQL Server type. The SQL Server ODBC driver will convert the C data type to one of the appropriate sql_variant subtypes.