Introduction to OLE DB for OLAP
OLE DB for OLAP is designed as an extension of OLE DB that allows you to access both relational and multidimensional data stores. A relational data store stores data that is logically related and exposes it as a set of two-dimensional tables; a multidimensional data store stores the data in inherently multidimensional structures.
The following illustration shows this extension of the OLE DB architecture. The consumer can use the OLE DB resources in the COM or COM+ environment to connect to an OLAP-specific provider, following the typical OLE DB architectural model.
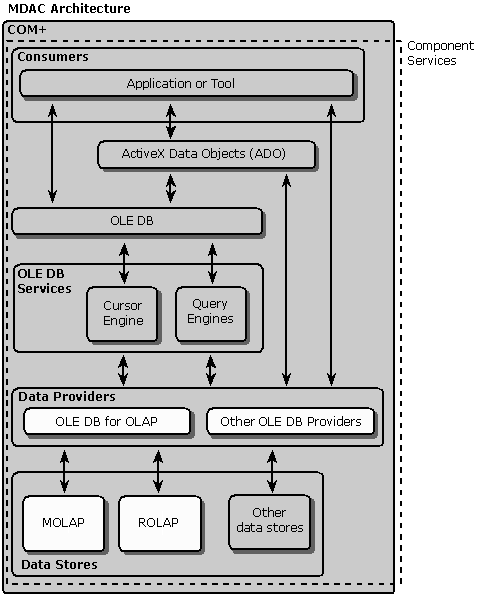
OLE DB for OLAP leverages the OLE DB object model and defines specific interfaces that enable representation, expression, transportation, and efficient navigation of multidimensional data within COM. These interfaces, IMDDataset, IMDFind, and IMDRangeRowset, can interconnect so that the same interfaces are applicable among data providers and various levels of service component implementation. As a result, the number of OLE DB for OLAP–specific objects and interfaces is minimized.
The OLE DB for OLAP interfaces cover common consumer (or client application) requirements for processing multidimensional data, but these interfaces are implemented so that existing multidimensional data providers (MDPs) can expose OLE DB for OLAP without making changes at the server level.
By supporting existing mechanisms for updating OLE DB rowsets, OLE DB for OLAP providers can define new interfaces, as well as language clauses for updating results. Vendors can define proprietary language extensions for data definition language (DDL) functionality.
As a means to access and manipulate data, OLE DB for OLAP uses MDX. MDX is a customized query syntax for multidimensional expressions that is explained in detail in Chapter 25: Multidimensional Expressions.
OLE DB for OLAP is designed to enforce symmetry across all dimensions. For example, interfaces expose measurements, such as percent growth over time, as a dimension with functionality equivalent to all other dimensions. Therefore, it is possible to use any of the OLE DB for OLAP–defined functions on any type of dimension to obtain desired results.
OLE DB for OLAP is optimized for both of the following configurations:
- The MDP and the consumer run in the same process in one process space, such as an OLE DB for OLAP MDP and the query engine of an RDBMS running in the same process.
- Service components that expose OLE DB for OLAP interfaces and also consume other OLE DB interfaces.
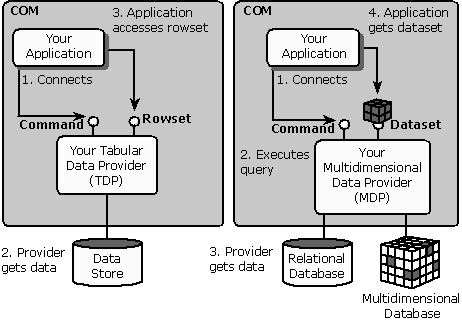
Conceptually, multidimensional data is represented as a cube. The cube—or more appropriately, the hypercube—is also the central metadata object recognized by OLE DB for OLAP and is the representation of multidimensional data in rowset form. It is expressed through the dataset object, which is specific to OLE DB for OLAP. Consumers can expose the data as rowsets by connecting to a tabular data provider (TDP) or a multidimensional data provider (MDP), as shown in the following illustration.
The Programming and Object Models
OLE DB for OLAP follows the basic programming model set forth in OLE DB:
- Locate a data source. The enumerator object is used to locate the provider (TDP or MDP) associated with the targeted data store and to create the OLE DB data source object, which is then used to create the session object. However, in OLE DB for OLAP, the consumer must be able to easily determine the type of a given data source object—whether TDP, MDP, or both.
- Specify a session, which is the context on a connection to a data source in which transactions or operations are created.
- Request a rowset object, typical of OLE DB, or, specific to OLE DB for OLAP, request data through a command by using multidimensional expressions (MDX), which comprise an OLE DB for OLAP–provided language used to manipulate the results in a dataset object.
- Present data through either the rowset object (using a TDP) or the dataset object (using an MDP and MDX). The rowset object is used to present multidimensional data in a flattened form.
- Pass a return code that reports whether the method succeeded or failed, optionally generating an error object containing details about a failed operation.
OLE DB Extensions for OLAP
OLE DB for OLAP defines expressions, interfaces and methods that enable providers to expose the multidimensional schemas of a multidimensional data store. It expresses those schemas as a set of cubes, which in turn enables the consumer to manipulate these cubes as schema rowsets.
Using the following extensions, you can build OLAP applications that leverage the OLE DB architecture:
- The dataset object. Execution of a user's query results in a dataset object, which consists of a set of value points, or cells, taken from the data store cube (or cubes) and built into the dataset cube. This is similar to a query in a relational database system, where the query encompasses one or more tables and returns a result set that has the same structure as that of a table. The dataset object exposes standard OLE DB interfaces and three OLE DB for OLAP–specific ones: IMDDataset, IMDFind, and IMDRangeRowset. OLE DB for OLAP also allows you to view a dataset, represented by a cube, in a flattened form. The process of flattening a dataset to produce a rowset can create a variety of views in tabular, rowset form.
- The range rowset object. When cell data requires updating, it is actually the range rowset object that is updated by using methods similar to those used on any other OLE DB rowset object. In a range rowset, each row corresponds to a cell in the dataset and each selected cell property appears as a column in the rowset. For more information, see "Working with Cell Data" in Chapter 24: Rowsets in OLE DB for OLAP.
- Multidimensional schema rowsets for OLE DB for OLAP. Consumers can get data store information about the cubes, dimensions, hierarchies, levels, and members by browsing multidimensional schema rowsets using the IDBSchemaRowset interface. For information about how OLE DB for OLAP exposes and uses these multidimensional schemas as schema rowsets, see "Multidimensional Schemas" in Chapter 22, "OLE DB for OLAP Concepts."
- Multidimensional expressions (MDX). For specifying a dataset object, OLE DB for OLAP defines a rich syntax of multidimensional expressions, which can be understood as a set of macros defined on top of the SQL language. Although these macros are generally useful for querying a multidimensional data store, their precise semantics are defined by means of their SQL language mappings.
- Executing client-side processes. OLE DB for OLAP also extends the capability of existing OLAP tools and applications by implementing the ACTIONS schema rowset, which allows a standard mechanism of integrating client actions or processes. It is also possible to annotate values in a schema rowset and store those values with the data, providing more benefits to the user.

