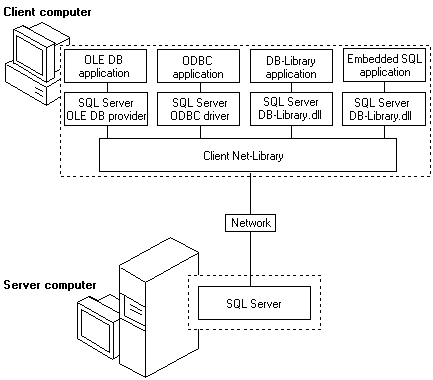
Client Components
Clients do not access Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2000 directly; instead, clients use applications written to access the data in SQL Server. These can include utilities that come with SQL Server 2000, third-party applications that access SQL Server 2000, in-house applications developed by programmers at the SQL Server 2000 site, or Web pages. SQL Server 2000 can also be accessed through COM, Microsoft ActiveX®, or Windows® DNA components.
SQL Server 2000 supports two main classes of applications:
- Relational database applications that send Transact-SQL statements to the database engine; results are returned as relational result sets.
- Internet applications that send either Transact-SQL statements or XPath queries to the database engine; results are returned as XML documents.
Relational Database APIs
Relational database applications are written to access SQL Server 2000 through a database application programming interface (API). A database API contains two parts:
- The language statements passed to the database.
The language by relational SQL Server 2000 applications is Transact-SQL. Transact-SQL supports all SQL-92 Entry Level SQL statements and many additional SQL-92 features. It also supports the ODBC extensions to SQL-92 and other extensions specific to Transact-SQL.
- A set of functions or object-oriented interfaces and methods used to send the language statements to the database and process the results returned by the database.
Native API Support
Native API support means the API function calls are mapped directly to the network protocol sent to the server. There is no intermediate translation to another API needed. SQL Server 2000 provides native support for two main classes of database APIs:
- OLE DB
SQL Server 2000 includes a native OLE DB provider. The provider supports applications written using OLE DB, or other APIs that use OLE DB, such as ActiveX Data Objects (ADO). Through the native provider, SQL Server 2000 also supports objects or components using OLE DB, such as ActiveX, ADO, or Windows DNA applications.
- ODBC
SQL Server 2000 includes a native ODBC driver. The driver supports applications or components written using ODBC, or other APIs using ODBC, such as DAO, RDO, and the Microsoft Foundation Classes (MFC) database classes.
An example of nonnative support for an API would be a database that does not have an OLE DB provider, but does have an ODBC driver. An OLE DB application could use the OLE DB provider for ODBC to connect to the database through an ODBC driver. This provider maps the OLE DB API function calls from the application to ODBC function calls it sends to the ODBC driver.
Additional SQL Server API Support
SQL Server 2000 also supports:
- DB-Library
DB-Library is an API specific to SQL Server 2000 and Microsoft SQL Server. SQL Server 2000 supports DB-Library applications written in C. DB-Library has not been extended beyond the functionality it had in Microsoft SQL Server version 6.5. Existing DB-Library applications developed against earlier versions of Microsoft SQL Server can be run against SQL Server 2000, but many features introduced in SQL Server 2000 and SQL Server version 7.0 are not available to DB-Library applications.
- Embedded SQL
SQL Server 2000 includes a C precompiler for the Embedded SQL API. Embedded SQL applications use the DB-Library DLL to access SQL Server 2000.
XML Access
Internet applications retrieve results in the form of XML documents rather than relational result sets. The applications execute either XPath queries or Transact-SQL statements that use the FOR XML clause to specify that results be returned as XML documents. If you define a virtual root on a Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) that points to an instance of SQL Server 2000, IIS applications can use three mechanisms for executing XPath queries or Transact-SQL statements:
- Execute a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that references the virtual root and contains an XPath query or Transact-SQL statement with FOR XML.
- Use the ADO API to execute an XPath query to Transact-SQL statement with FOR XML.
- Use the OLE DB API to execute an XPath query to Transact-SQL statement with FOR XML.
Client Communications
The Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server 2000, the SQL Server 2000 ODBC driver, and DB-Library are each implemented as a DLL that communicates to SQL Server 2000 through a component called a client Net-Library.